链表是由一系列的结点组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包含两部分:数据域与指针域。数据域存储数据元素,指针域存储下一结点的指针。在python中需要通过定义类来实现链表的操作。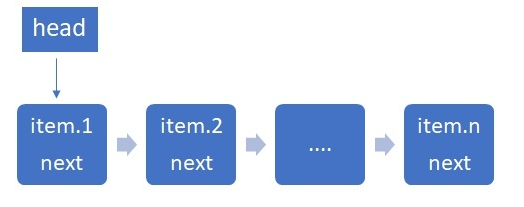
head 保存首地址,item 存储数据,next 指向下一结点地址。
相关讲解参考:Python 数据结构之链表 - 知乎
移除链表元素
题目
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1: 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2: 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3: 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
解题
链表需要具有首地址指针head,可以设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
dummy_head = ListNode(next=head) #添加一个虚拟节点
cur = dummy_head
while(cur.next!=None):
if(cur.next.val == val):
cur.next = cur.next.next #删除cur.next节点
else:
cur = cur.next
return dummy_head.next设计链表
题目
在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
- addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
- addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
- addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
- deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
解题
需要先定义节点的类,然后在链表的初始化里定义一个虚拟的头结点。
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, x=0, next = None):
self.val = x
self.next = next
class MyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = Node()
self.size = 0
def get(self, index: int) -> int:
if index < 0 or index >= self.size:
return -1
cur = self.head.next
while(index):
cur = cur.next
index -= 1
return cur.val
def addAtHead(self, val: int) -> None:
headnode = Node(val)
headnode.next = self.head.next
self.head.next = headnode # 只有head.next才是链表的第一个节点
self.size += 1
def addAtTail(self, val):
new_node = Node(val)
cur = self.head
while(cur.next):
cur = cur.next
cur.next = new_node
self.size += 1
def addAtIndex(self, index, val):
if index < 0:
self.addAtHead(val)
return
elif index == self.size:
self.addAtTail(val)
return
elif index > self.size:
return
node = Node(val)
pre = self.head # pre的用法,不是直接next,根据不同功能选择辅助变量
while(index):
pre = pre.next
index -= 1
node.next = pre.next
pre.next = node
self.size += 1
def deleteAtIndex(self, index):
if index < 0 or index >= self.size:
return
pre = self.head
while(index):
pre = pre.next
index -= 1
pre.next = pre.next.next
self.size -= 1
# Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyLinkedList()
# param_1 = obj.get(index)
# obj.addAtHead(val)
# obj.addAtTail(val)
# obj.addAtIndex(index,val)
# obj.deleteAtIndex(index)翻转链表
题目
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例: 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
解题
第一种比较常规的解法,利用双指针来进行求解,在迭代的过程中实现对链表的逐步反转。
以1,2,3,4,5来举例的话,迭代的结果: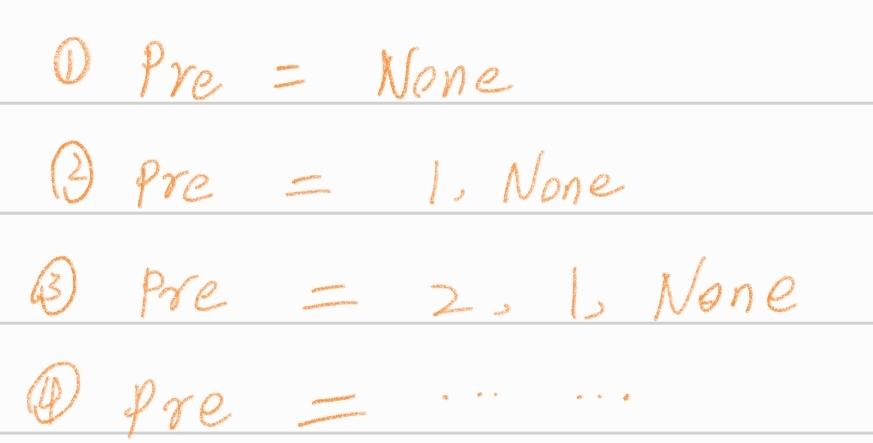
# 双指针法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
cur = head # 初始化为头节点
pre = None # 初始化为空
while(cur != None):
temp = cur.next # 暂存下一个节点位置
cur.next = pre
pre = cur # 指针迭代
cur = temp # 指针迭代
return pre# 递归法(按照双指针法的思路)
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverse(pre,cur):
if not cur: # 终止条件
return pre
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
return reverse(cur,tmp) # 类比迭代的赋值
return reverse(None,head) # 初始设置两两交换链表中的节点
题目
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
输入: head = [1,2,3,4]
输出: [2,1,4,3]
解题
需要创建虚拟头节点来方便操作,使用画图的方式厘清节点之间先后交换的关系。两个节点两个节点进行处理。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
headpoint = ListNode(next = head)
pre = headpoint
# 判断当前是否存在两个节点可以进行交换
while pre.next and pre.next.next:
cur = pre.next
cur2 = pre.next.next # cur和cur2是当前要处理的两个节点
cur.next = cur2.next
cur2.next = cur
pre.next = cur2
pre = pre.next.next # 移动节点处理的顺序,进两位
return headpoint.next # 返回头节点的内容删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头节点。
解题
双指针的经典应用,如果要删除倒数第n个节点,让fast移动n步,然后让fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向链表末尾。删掉slow所指向的节点就可以了。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
head_dummy = ListNode()
head_dummy.next = head
slow, fast = head_dummy, head_dummy
while(n>=0): #fast先往前走n+1步
fast = fast.next
n -= 1
while(fast!=None):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
#fast 走到结尾后,slow的下一个节点为倒数第N个节点
slow.next = slow.next.next #删除
return head_dummy.next链表相交
题目
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。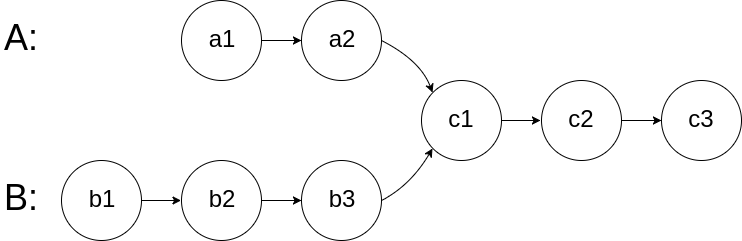
解题
首先计算链表的长度,通过其相交节点后一样的特性,让长的链表的指针进行移动,然后两个链表来进行比较。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
lenA, lenB = 0, 0
cur = headA
while cur:
cur = cur.next
lenA += 1
cur = headB
while cur:
cur = cur.next
lenB += 1
curA, curB = headA, headB
if lenB < lenA:
curA, curB = curB, curA
lenA, lenB = lenB, lenA
for _ in range(lenB - lenA):
curB = curB.next
while curA:
if curA == curB:
return curA
else:
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
return None



